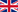
MAIN WEATHER AND CLIMATE TRAITS IN THE NORTHEN HEMISPHERE AS OF JUNE 2019
Air Temperature
Record-breaking heat that settled in the southern ETR at the end of spring routinely migrated to the beginning of summer. All through the first decade, new air temperature maxima were recorded in the Stavropol and Krasnodar Territories, Crimea and North Caucasus. In the middle of the decade, the heat spread to the central and south-western regions where new records were set as well. The thermometer readings in the Moscow, Kaluga and Ryazan Regions and in some other ones steadily rose to above +30°. The decade-averaged air temperatures exceeded their normal values by 3-5° or more everywhere from Karelia to the Black Sea. The temperature anomalies in this decade were even larger in Yakutia, Eastern Siberia and the north of the Far East (up to 5-8° and above). But the weather was cold between these foci of heat, namely, in the Urals, in Western Siberia, in the Upper Volga and in the south of the Far East.
The same picture was observed in the second decade when the unprecedented temperature maxima were recorded in the ETR and in the east of the country. In this decade, the anomalies became even higher: up to and above +6-8° in the European part, and up to and above +6-10° along the Arctic coast from Taimyr to Chukotka.
MAIN WEATHER AND CLIMATE TRAITS IN THE NORTHEN HEMISPHERE AS OF MAY 2019
Air Temperature
In the west of Russia, the anomalously cold weather that settled there in the end of April preserved in the beginning of May. Cold air from European countries was still flowing to Russia. Sub-normal temperatures recorded in the Leningrad, Pskov and Novgorod Regions culminated in night frosts and record-breaking temperature minima in the Kaliningrad Region. The frosts and unprecedented colds in the first decade were also observed in Central Russia, the Upper Volga Region and the Urals. Of all the ETR, the abnormal warmth at that time was only in the south of Russia (the Krasnodar and Sevastopol Territories) and in the Middle and Lower Volga Regions: there, the thermometer readings could reach as high as +30°.
In contrast to this, the weather was very warm in the east of the country. New air temperature maxima were repeatedly recorded all the way from the Urals to Chukotka and Primorye. Sometimes, the air heated to +20° in Yakutia and almost to +30° in the south of the Urals and of the Far East. The normal values of decade-averaged air temperatures in the Urals and in the north of the Far East were exceeded by 5-7°.
Further on, such abnormal high-temperature background started to fade throughout the country, and the anomalies normally decayed to at most +2…4° in the second and third decades. Spots of anomalous heat creating new temperature maxima still survived in the Volga and Cis-Ural Regions in the second decade, but the bitter arctic cold rushing down to the ETR and Siberia in the third decade brought frosts and even record-breaking colds to Central Russia, to the west of the ETR and to the south of Siberia. In the second decade, the air temperature anomalies in the south areas of the Krasnoyarsk Territory, in Khakassia and Tyva were -2…-5°.